| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 |
- 세그먼트 트리
- 자료 구조
- 구현
- js
- 토이 프로젝트
- REACT
- JavaScript
- 수학
- 엔트리포인트
- react-three/fiber
- Next.js
- HTML5
- 코딩일기
- styled-components
- 해시를 사용한 집합과 맵
- State
- 시뮬레이션
- 브루트포스
- 백준
- poiemaweb
- three.js
- 개발 회고
- 자바스크립트
- 모던 자바스크립트 튜토리얼
- 기본 문법
- 티스토리챌린지
- 프론트엔드
- 회고
- 자바
- 오블완
- Today
- Total
코딩하는 고릴라
[Algorithm] 힙 구현 (Javascript) 본문
힙
완전 이진 트리 구조를 가지며 정해진 조건에 따라 항상 정렬된 상태를 유지하는 비선형 자료구조
항상 정렬되어 있는 상태를 유지하기 때문에 최대값, 최소값 등을 수시로 조회해야 할 경우 속도상 이점을 가집니다.
🐇 시간복잡도
- 조회 : O(1)
- 삽입 : O(logN)
- 삭제 : O(logN)
🦙 구현
자바스크립트에서 힙 자료구조는 제공되지 않기 때문에 직접 구현하는 방법에 대해 학습해봤습니다.
조회, 삽입, 삭제 메서드 위주로 구현해 보도록 하겠습니다.
여기서는 최대값을 바로 바로 뽑아낼 수 있는 최대힙을 구현해 보겠습니다.
1. 기본 구조
class MaxHeap {
constructor(){
this.storage = [null];
}
}1번 인덱스부터 사용하기 위해 0번 인덱스는 null 값을 저장해두었습니다.
2. 조회 : peek()
class MaxHeap {
// ..
peek(){
return this.storage[1] ?? null;
}
}힙 배열 내에서 가장 상층 (루트 노드)에 위치한 값을 리턴하도록 합니다.
배열의 사이즈가 1일 경우에는 undefined가 리턴되므로 nullish 병합 연산자를 이용해 명시적으로 null을 리턴하도록 했습니다.
3. 삽입 : push(value)
class MaxHeap {
// ..
push(value){
const heap = this.storage;
heap.push(value);
this.heapifyUp(); // 아래에서 추가적으로 작성할 메서드
return heap;
}
}
트리의 가장 뒤쪽에 입력받은 value를 삽입합니다.
그 후 아래에서 작성할 heapifyUp 메서드를 통해 트리를 정렬된 상태로 유지시킵니다.
3-1. 정렬 : heapifyUp()
class MaxHeap {
// ..
heapifyUp() {
const heap = this.storage;
let child = heap.length - 1; // 트리 가장 뒤쪽에 있는 인덱스
let parent = Math.floor(child / 2); // 위 child의 부모 노드
// 자식 노드의 값이 부모 노드의 값보다 클 때
while (parent > 0 && heap[child] > heap[parent]) {
// 두 노드 간 위치 변경
let tmp = heap[parent];
heap[parent] = heap[child];
heap[child] = tmp;
// 자식, 부모 노드 갱신
child = parent;
parent = Math.floor(parent / 2);
}
}
}


트리의 가장 뒤쪽에 삽입된 값과 그 부모 노드의 값을 비교하여 위치를 변경할지 말지 판단합니다.
삽입된 값이 부모 노드 값보다 크다면 위치를 바꾸고, 이를 루트 노드 혹은 부모 노드가 자식 노드보다 더 작을 때까지 계속해서 반복합니다.
4. 삭제 : pop()
class MaxHeap {
// ..
pop() {
const heap = this.storage;
if (heap.length === 1) return null; // 트리에 null만 저장되어 있는 상태
if (heap.length === 2) return heap.pop(); // 트리에 하나의 값만 저장되어 있는 상태
const returnValue = heap[1]; // 루트 노드의 값을 반환값으로 미리 지정
heap[1] = heap.pop(); // 트리의 가장 뒤쪽에 있는 값을 루트 노드로 이동 (가장 작은 값을 루트 노드로 이동)
this.heapifyDown(); // 자식 노드보다 작은 값을 아래로 내리는 작업
return returnValue;
}
}
루트 노드의 값을 반환하고, 정렬 상태를 유지하기 위한 heapifyDown 메서드를 호출합니다.
4-1. 정렬 : heapifyDown()
class MaxHeap {
// ..
heapifyDown() {
const heap = this.storage;
let parent = 1;
let child = parent * 2;
if (child + 1 < heap.length && heap[child + 1] > heap[child]) {
child += 1;
}
while (child < heap.length && heap[parent] < heap[child]) {
let tmp = heap[parent];
heap[parent] = heap[child];
heap[child] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = parent * 2;
if (child + 1 < heap.length && heap[child + 1] > heap[child]) {
child += 1;
}
}
}
}
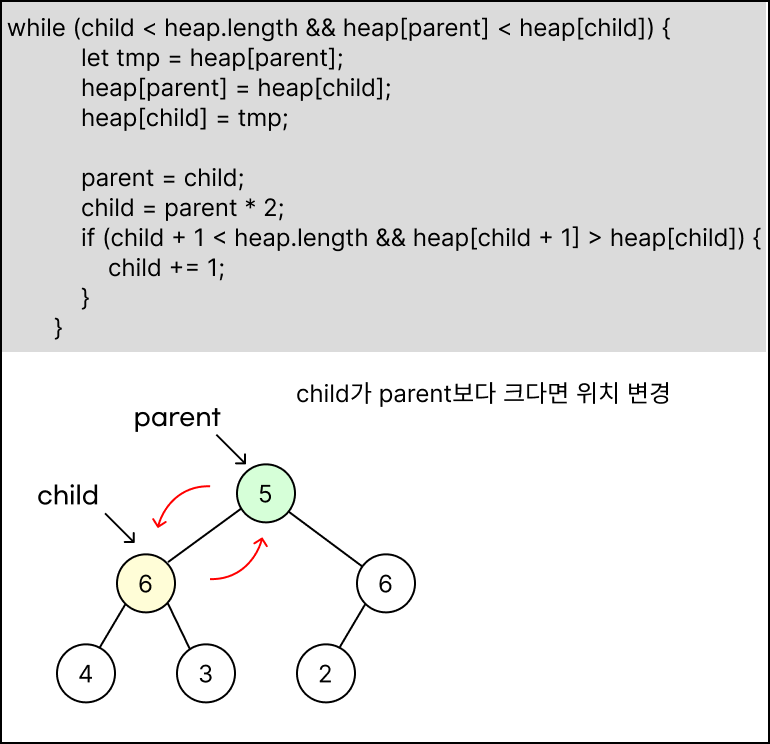

트리의 루트 노드와 그 자식 노드 중 더 큰 값을 가진 자식 노드와 비교하여 위치를 변경할지 판단합니다.
부모 노드의 값이 자식 노드보다 작다면 위치를 바꾸는 과정을 리프 노드까지 반복합니다.
전체 코드
class MaxHeap {
constructor() {
this.storage = [null];
}
size() {
return this.storage.length;
}
push(value) {
const heap = this.storage;
heap.push(value);
this.heapifyUp();
return heap;
}
pop() {
const heap = this.storage;
if (heap.length === 1) return null;
if (heap.length === 2) return heap.pop();
const returnValue = heap[1];
heap[1] = heap.pop();
this.heapifyDown();
return returnValue;
}
peek() {
return this.storage[1] ?? null;
}
heapifyUp() {
const heap = this.storage;
let child = heap.length - 1;
let parent = Math.floor(child / 2);
while (parent > 0 && heap[child] > heap[parent]) {
let tmp = heap[parent];
heap[parent] = heap[child];
heap[child] = tmp;
child = parent;
parent = Math.floor(parent / 2);
}
}
heapifyDown() {
const heap = this.storage;
let parent = 1;
let child = parent * 2;
if (child + 1 < heap.length && heap[child + 1] > heap[child]) {
child += 1;
}
while (child < heap.length && heap[parent] < heap[child]) {
let tmp = heap[parent];
heap[parent] = heap[child];
heap[child] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = parent * 2;
if (child + 1 < heap.length && heap[child + 1] > heap[child]) {
child += 1;
}
}
}
}
실행 결과
function solution() {
let heap = new MaxHeap();
heap.push(1);
heap.push(4);
heap.push(2);
heap.push(7);
heap.push(5);
console.log(heap.pop()); // 7
console.log(heap.pop()); // 5
console.log(heap.pop()); // 4
console.log(heap.pop()); // 2
console.log(heap.pop()); // 1
console.log(heap.pop()); // null
}
'Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Algorithm] 큐 구현(Javascript) (0) | 2023.11.13 |
|---|---|
| [Algorithm] 그래프 표현 - 인접 리스트 구현(JAVA) (4) | 2023.10.05 |


